Nearly 1.6 billion people are affected by anemia, and many of them end up in the hospital needing skilled nursing care. Anemia is not just about labs, but it is about identifying symptoms, implementing interventions, and improving patient outcomes. So, how nurses manage anemia effectively in fast paced clinical setting, the answer is Nursing Care Plan (NCP), which helps them to assess, plan, and intervene carefully.
Do you know that SkillGigs is an AI platform that matches travel nurses with their dream contracts? Sign up with SkillGigs now and get a $500 bonus once you sign your first contract with us. explore high paying travel nursing jobs here.
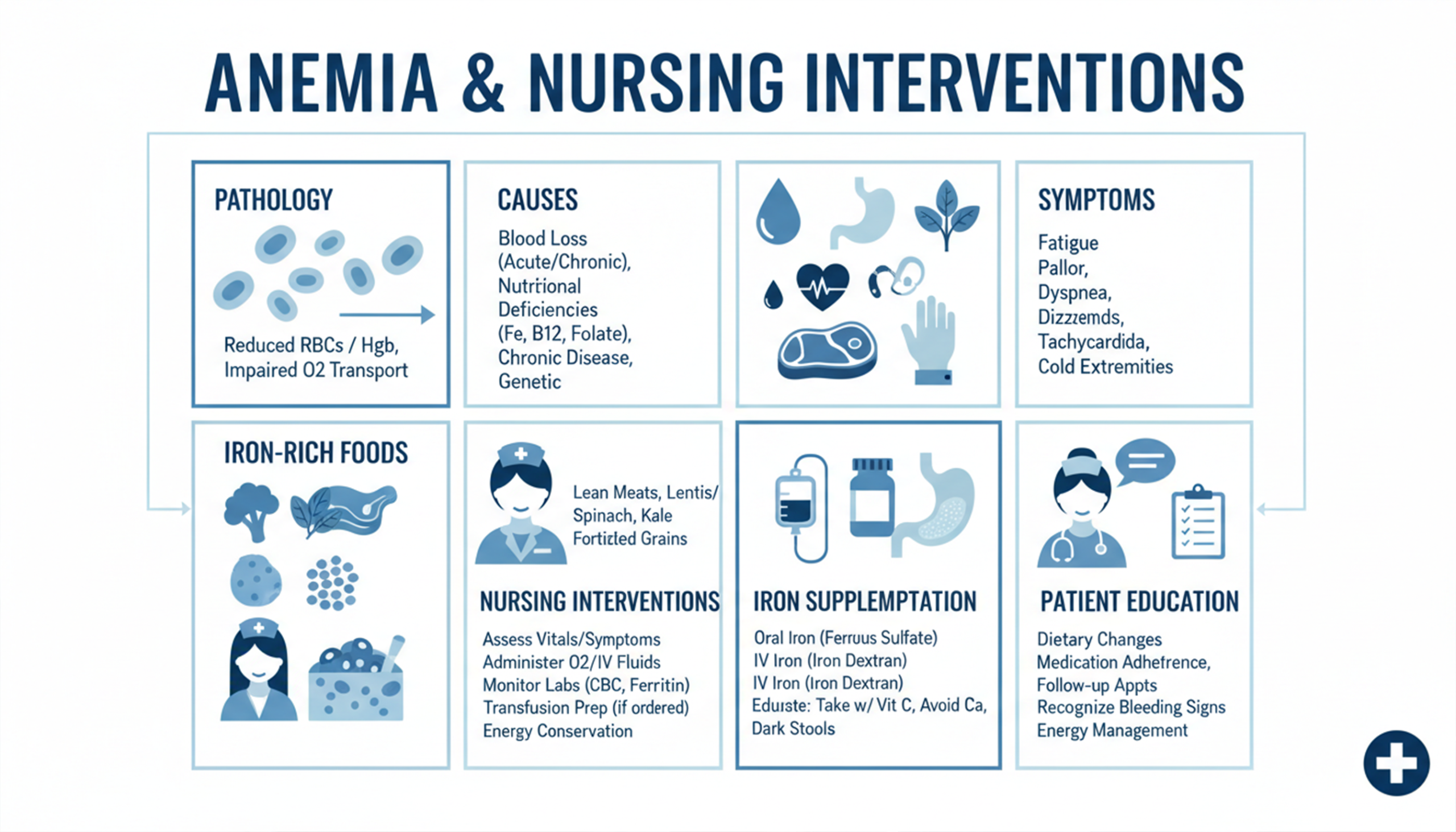
What is Anemia?
Anemia is a medical condition where the body doesn’t have enough hemoglobin (healthy red blood cells) to carry oxygen to tissue. Common causes of anemia include iron deficiency, chronic kidney disease, hemolysis, and acute or chronic blood loss, etc. Common signs and symptoms of anemia are fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness, etc.
Different types of anemia
There are different types of anemia:
- Iron deficiency anemia: Low iron due to reduced hemoglobin.
- Vitamin deficiency anemia: Such as vitamin B12 deficiency and folate deficiency
- Aplastic Anemia: Bone marrow failure
- Hemolytic Anemia: premature destruction of red blood cells (RBCs)
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Genetic Hemoglobin Disorder
- Thalassemia: Inherited hemoglobin synthesis disorder
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: chronic illness
- Acute Blood Loss Anemia: Due to trauma or injury
- Chronic Kidney Disease–Related Anemia: Low erythropoietin production
- Megaloblastic Anemia: Impaired DNA synthesis
Nursing care plan (NCP) for anemia with an example
The Nursing Care Plan (NCP) is a systematic approach that nurses use to identify patients’ problems, set priorities, and evaluate outcomes. The key components of the nursing care plan are as follows:
- Assessment
- Diagnosis
- Goals
- Nursing interventions
- Evaluation
Assessment
The first step in the nursing care plan is assessment, which includes both subjective and objective data. The nursing care plan for anemia involves the following:
Subjective data: It is the information that the patient tells the nurse. For example, a patient tells the nurse about fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, weakness, and chest discomfort.
Objective data: Objective data refers to what the nurse can see, measure, and verify. For example, in the case of anemia, it is the following:
- Hemoglobin level: 7.5 g/dL
- Blood pressure: 90/60 mmHg
- Heart rate: 112 bpm
- Oxygen saturation: 90% on room air
- Pale skin and nails
Tip to remember subjective and objective data
- Subject = Say
- Objective = Observes
Nursing diagnosis of anemia
The second step of the nursing care plan (NCP) is nursing diagnosis, which is the clinical judgment made by nurses about the patient’s health problems using NANDA-I standardized nursing diagnoses.
NANADA-I stands for North American Nursing Diagnosis Association – International. Common nursing diagnoses for anemia in patients include the following:
- Fatigue due to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of blood.
- Reduce stamina and energy due to low blood cell count.
- Imbalanced nutrition
- Risk of impaired tissue perfusion related to decreased hemoglobin levels.
Goals (NCP for anemia)
The next step for the nursing care plan (NCP) is GOALS that include both short- and long-term GOALS. The GOALS should be SMART, which stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time Bound.
Short-term goals for anemia:
- Patients will feel less tired after 48 hours.
- Vital signs will be stable during activity.
Long-term goals for treating anemia:
- The patient’s hemoglobin levels will become normal after treatment.
- Patient will continue with daily activities without shortness of breath.
Nursing interventions for anemia
Intervention in nursing is the action that nurses take to help patients achieve the goals of the nursing care plan. Intervention can be independent, dependent, or collaborative.
Independent: Nurses don’t need a doctor’s order, for example, to encourage rest periods for the patient.
Dependent: Nurses require a doctor’s order to carry out the plan, for example, administering iron medication to the patient.
Collaborative: Nurses work with other healthcare professionals to achieve the desired goals and treat patients, for example, working with dieticians to give patient iron rich diet.
Evaluation of the nursing care plan for anemia
Evaluation means determining if the goals were achieved or not, and whether there is any need for adjustment. The evaluation will include the following:
- Reassessing fatigue
- Monitoring hemoglobin
- Observing the patient’s response to treatment
- Documenting and revising the care plan.
Conclusion
Anemia affects millions of people worldwide; it is a common yet serious condition and should be treated on time to avoid complications. To manage anemia effectively in this fast-paced clinical environment, nurses use the NCP (Nursing Care Plan).NCP helps nurses to assess, diagnose, intervene, and evaluate effectively to ensure patients recover safely.
Sign up with SkillGigs and become part of our travel nursing world, an AI platform that connects you with rewarding, high-paying travel nursing contracts. Join now and get a $500 bonus when you sign your first contract.