Those zig-zag lines on fetal monitoring are not just lines but messages, and one wrong interpretation of a fetal heart rate strip can change everything. Therefore, accurate fetal heart rate interpretation is a crucial skill that every labor and delivery nurse should possess. VEAL CHOP is a mnemonic that helps nurses decide these messages quickly, confidently, and safely. In this blog, we will discuss VEALCHOP nursing in detail and provide real-life examples.
Before we start, are you a nurse looking to level up your career? Join SkillGigs now and become part of our travel nursing world, where you can find high-paying travel nursing contracts.
What does VEAL CHOP mean in nursing?
VEAL CHOP is a mnemonic that helps nurses and travel nurses interpret fetal heart rate patterns during labor. Labor and delivery nurses monitor the heart rate during pregnancy and labor to check how well the baby is doing inside the womb, i.e., making sure the baby is getting enough oxygen and is not under stress. VEAL CHOP is a memory aid that helps nurses recall how to interpret the different fetal heartbeat patterns. Here is the breakdown of the VEAL CHOP mnemonic in nursing:
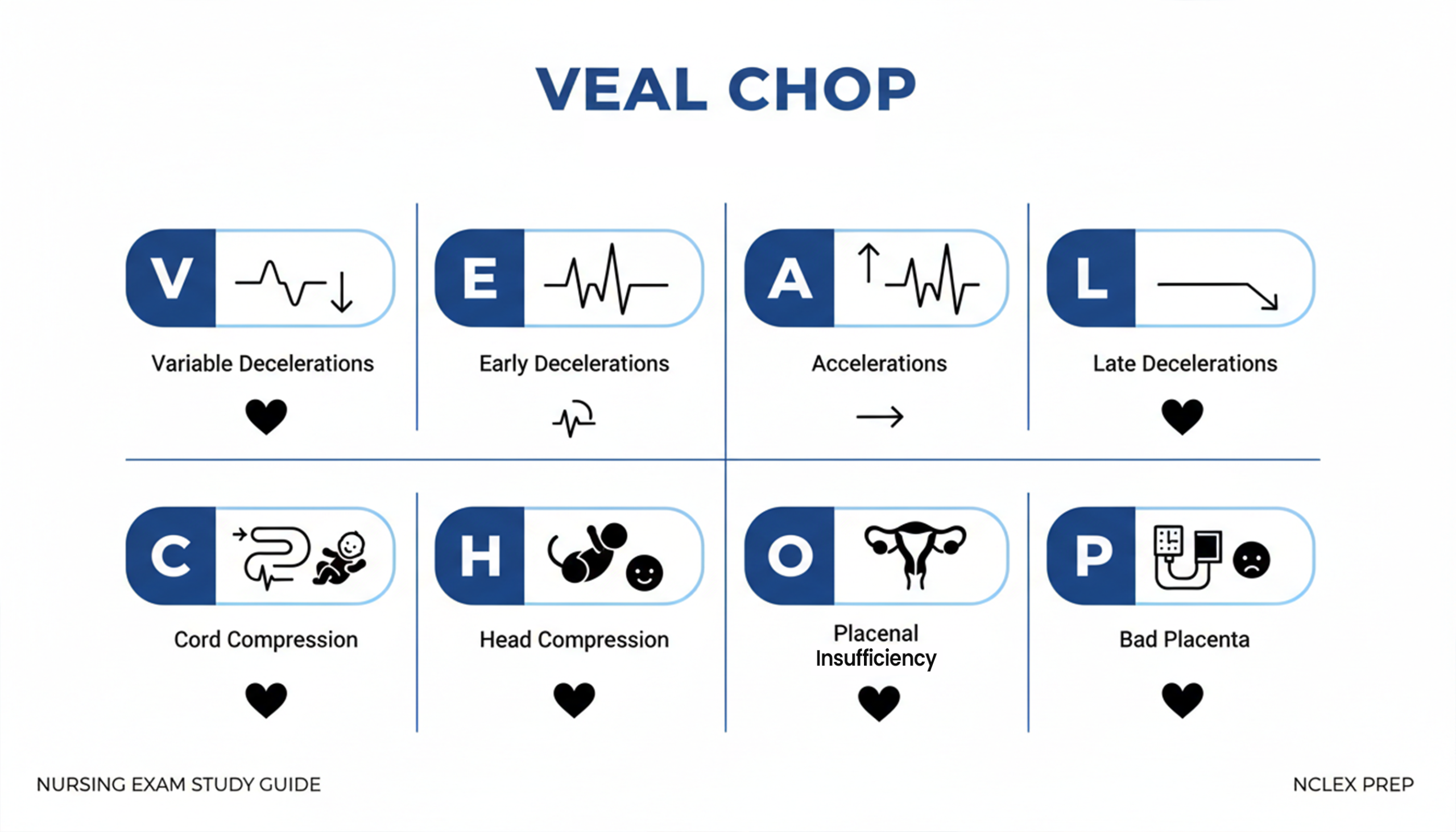
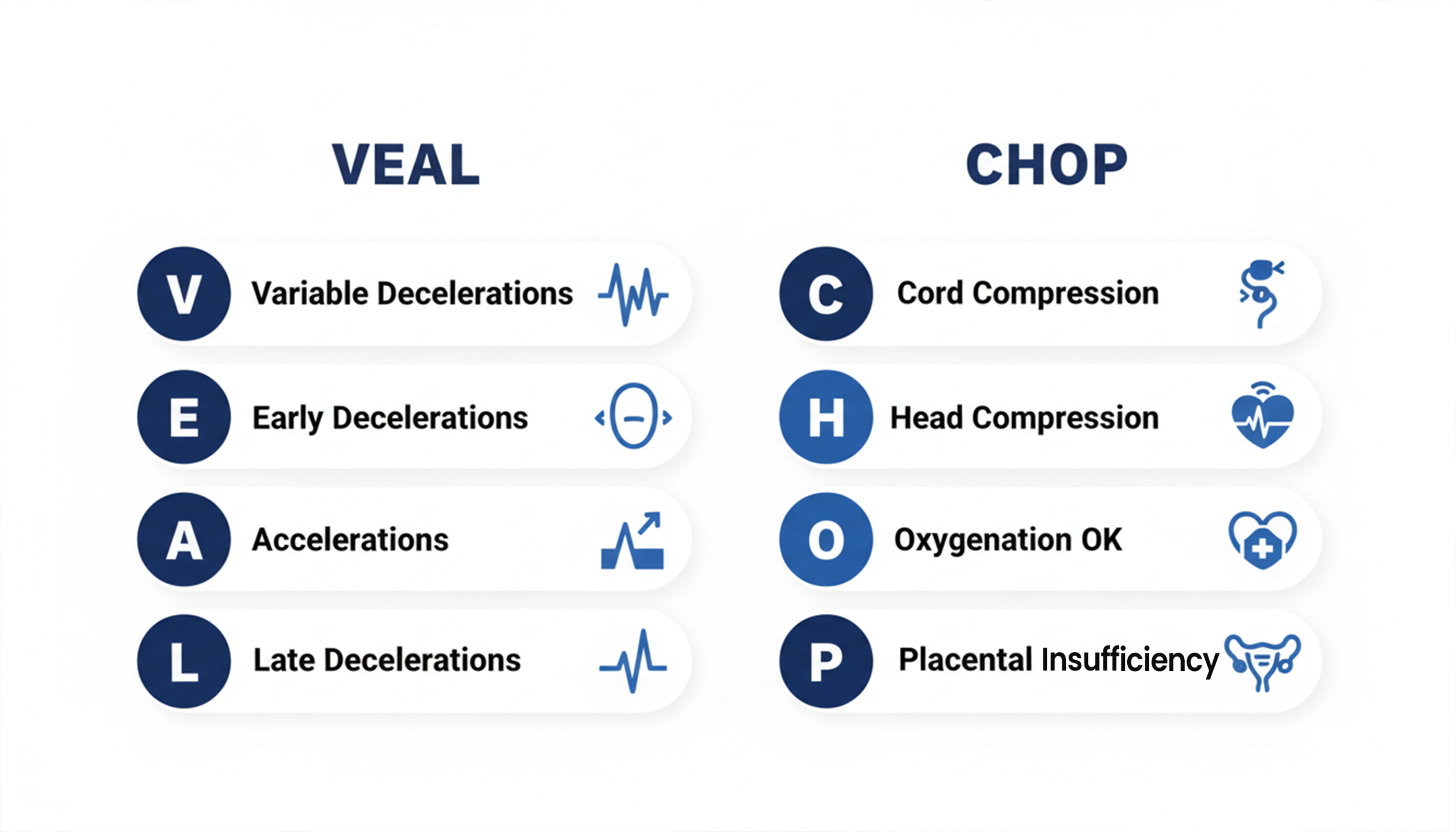
VEAL (Fetal Heart Rate Patterns)
V: Variable decelerations
E: Early decelerations
A: Accelerations
L: Late decelerations
CHOP (Meaning of those patterns)
C: Cord compression
H: Head compression
O: Okay / Oxygenated
P: Placental insufficiency
Meaning of VEAL CHOP
V (Variable decelerations) → C (Cord compression)
Baby gets oxygen and nutrients through the umbilical cord, and when this umbilical cord is compressed, less oxygen reaches the baby, resulting in the heart rate dropping. These heart rate drops are irregular patterns, which means the baby is not getting enough oxygen.
Common reasons are as follows:
- True knot in an umbilical cord.
- Umbilical cord prolapse.
- Nuchal cord, which means the umbilical cord is wrapped around the baby’s neck
- Low amniotic fluid
- The position of the mother or baby that might compress the umbilical cord.
- Uterine rupture
What to do?
- Check the cervix.
- Administer IV fluids to increase the blood flow to the cervix and placenta.
- Provide oxygen to the mother to improve the baby’s oxygen.
- If the baby shows the signs of continuous stress, then prepare for the cesarean birth.
Early Decelerations → Head Compression
This means that the baby’s heartbeat slows down before the strong contractions because the head is being pressed while moving down the birth canal. Early declarations are normal but not harmful.
Common reason why it happens:
- It is common during late labor.
- This can also happen in preterm labor.
What to do?
- Nurses can change the mother’s position to improve the oxygen and blood supply to the baby by making them lie on the left side with her knees to her chest.
- Nurses should continuously monitor the fetal heart to make sure the baby is ok.
Accelerations → OK
The baby’s heart starts beating faster, which is actually a good sign because it indicates that the baby is active and getting enough oxygen. The heartbeat increases 15 or more bpm for 15 seconds, which is a natural response.
What to do?
If it does not happen, then doctors can rock the mother’s womb, use a soft sound to wake the baby a little, or touch the baby’s head.
Late Decelerations → Placental Insufficiency
After contraction, the heart rate of the baby drops and lasts for 30 seconds or more. This means that the placenta is not giving enough oxygen to the baby, which can be dangerous if not treated on time.
What to do?
Positioning the mother by lying her on her side and bringing her knees up to improve the blood flow.
If the situation remains the same, then doctors can administer IV fluids, give oxygen, or even consider cesarean birth.
VEAL CHOP+ MINE
There is also an expanded version, which is VEAL CHOP MINE
V: Variable decelerations – C: Cord Compression – M: Move mother or change position
E: Early Decelerations – H: Head Compression – I: Identify Labor Progress
A: Acceleration – O: Okay – N: No Intervention needed
L: Late declaration – P: Placental insufficiency – E: Execute immediate actions
Importance of VEAL CHOP nursing
- Helps in rapid interpretation, which can help nurses to identify early if the baby is under any kind of stress.
- Nurses can take appropriate and timely actions to improve the outcomes.
- It also helps in recognizing the dangerous patterns early, and nurses can make a timely decision to save the baby and the mother.
- For nursing students, VEAL CHOP is the most commonly asked mnemonic in nursing school exams and the NCLEX-RN exam.
What is a normal fetal heart rate?
The normal fetal heart rate is 110 to 160 bpm, and temporary changes (accelerations) are common during birth.
Why do early declarations occur?
It occurs due to fetal head compression during labor.
What does VEAL CHOP stand for in OBGYN fetal heart monitoring?
The mnemonic VEAL CHOP stands for
Variable → Cord compression
Early → Head compression
Acceleration → Okay / good oxygenation
Late → Placental insufficiency
Conclusion
VEAL CHOP is a mnemonic in OB-GYN nursing that helps labor and delivery nurses to interpret fetal heart rate patterns during labor. It tells nurses the changes in the heartbeat, what may be causing it, and what actions to take to deliver safely. VEAL CHOP is also helpful for nursing students in nursing exams and NCLEX exams.
Before you start your travel nursing journey, sign up with SkillGigs and explore top travel nursing contracts with high pay. Get a $500 bonus once you sign your first assignment with us!