When building web applications, choosing the right framework can dramatically affect your development speed, scalability, and long-term maintainability. Django stands out as one of the most robust and versatile web frameworks in the world, powering everything from content-heavy sites to data-intensive platforms. But what exactly is Django, how does it work, and why do so many developers rely on it?
In this guide, we’ll explore what Django is, how it works, its core features, typical use cases, pros and cons, and why it remains a top choice for backend development in 2026.
What Is Django?
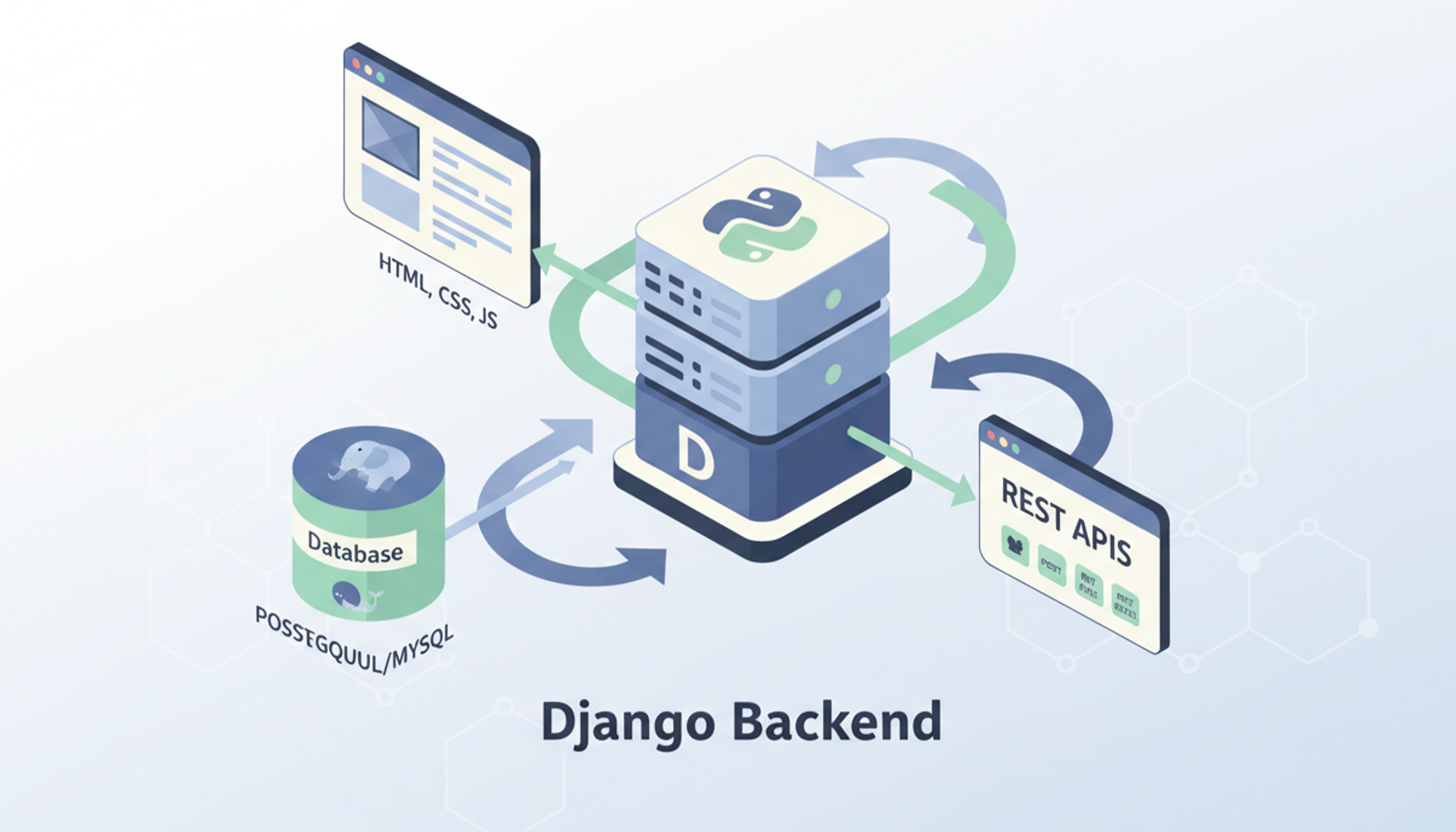
Django is an open-source web application framework written in Python that helps developers build powerful and scalable backend services quickly and efficiently. It is designed to make complex database-driven websites easier to develop by providing a set of reusable components and clear architectural patterns.
Originally inspired by Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural principles, Django uses a closely related approach often called Model-View-Template (MVT), which cleanly separates data, presentation, and request-handling logic for better organization and maintainability.
How Django Works
Django’s architecture revolves around the Model-View-Template (MVT) pattern:
- Model: Defines the structure of your application’s data and interacts with the database. Models map Python classes to database tables and handle data retrieval and manipulation.
- View: Processes HTTP requests, applies business logic, and returns HTTP responses. Views connect the database interaction performed by models with how data should be presented.
- Template: Renders HTML or other output formats based on data supplied by views. Django’s templating engine makes it easy to generate dynamic, data-driven pages.
- URL Routing: Django maps incoming web requests to the appropriate view functions using clean, developer-defined URL patterns.
This separation of concerns ensures that each part of your application — data, logic, and presentation — can evolve independently, improving both maintainability and scalability.
Key Features of Django
Django’s popularity comes from its rich set of built-in features that streamline web development:
- Object-Relational Mapping (ORM): Allows developers to interact with databases using Python classes rather than SQL queries, simplifying data access and migrations.
- Authentication and Authorization: Built-in systems for user login, permissions, and session management remove the need to build these from scratch.
- Admin Interface: An out-of-the-box dashboard for managing app data makes development and administration faster.
- URL Routing: A clean and flexible URL dispatcher helps create readable and scalable site structures.
- Templating Engine: Django’s template system makes generating dynamic content intuitive and efficient.
- Security: Built-in protections guard against common web vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and cross-site request forgery.
These capabilities mean Django developers can focus more on business logic and less on boilerplate infrastructure.
Why Developers Choose Django
Django is often chosen for backend development because it combines speed, security, and scalability:
Faster Development
Django includes reusable components (such as authentication, admin panels, and form handling) that accelerate development and reduce redundant coding. Its “batteries-included” philosophy helps teams ship functional applications more quickly.
Strong Python Ecosystem
Because Django is built on Python, one of the most popular and readable programming languages — it benefits from Python’s extensive libraries and community resources. This makes it ideal for integrating with tools for data science, AI, and automation.
Cost-Effective and Scalable
Django’s built-in capabilities and wide hosting support (including cloud platforms) make it cost-efficient for projects ranging from startups to enterprise systems. Many high-traffic sites use Django because it scales well with increased load.
Trusted by Big Tech
Worldwide tech leaders such as Instagram, Pinterest, Mozilla, Spotify, Dropbox, and NASA use Django to power key parts of their platforms, which speaks to the framework’s reliability and real-world strength.
Django for Frontend or Backend?
Although Django can generate HTML pages and render dynamic content, it is primarily a backend framework. Modern web applications often pair Django with frontend libraries or frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js to handle richer user interfaces.
This combination allows Django to manage server-side logic — like database operations and user authentication, while frontend frameworks handle interactive UI experiences.
Typical Use Cases for Django
Django is versatile and used across industries and application types, including:
- Financial platforms and analytics systems
- Customer relationship management (CRM) apps
- E-commerce and shopping portals
- Booking systems
- Enterprise dashboards and internal tools
- Advanced features such as email systems, data analysis utilities, and admin dashboards
- Its robustness makes it suitable for both simple web apps and complex data-driven systems.
Pros and Cons of the Django Framework
Pros
- Batteries-Included Framework: Comes with many ready-made tools that reduce development effort.
- Security: Provides strong defenses against common vulnerabilities.
- Community Support: A large, active community means more resources and faster problem-solving.
- Scalability: Can handle increased traffic and data volume with good architectural design.
Cons
- Monolithic Conventions: Django’s structure can feel rigid for developers used to more flexible frameworks.
- Steeper Learning Curve: Beginners may take longer to master its patterns and configuration.
- Not Always Ideal for Small Projects: For very lightweight apps, Django may feel too feature-rich.
Despite these challenges, Django still delivers strong value for a wide range of applications.
Conclusion
Django remains one of the most powerful and reliable web frameworks for backend development in 2026. Its rich feature set, scalability, and strong foundation in Python make it a go-to choice for developers building anything from simple sites to complex web platforms. Whether you’re creating APIs, enterprise systems, or large-scale applications, Django’s balance of structure and flexibility helps teams build faster and more securely than many alternatives.





